Database Design
이전에 설계한 API Design 을 기반으로 간단하게 Database 설계 및 sample data 를 추가해보자.
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `employee_directory`;
USE `employee_directory`;
--
-- Table structure for table `employee`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`first_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
--
-- Data for table `employee`
--
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES
(1,'Leslie','Andrews','leslie@luv2code.com'),
(2,'Emma','Baumgarten','emma@luv2code.com'),
(3,'Avani','Gupta','avani@luv2code.com'),
(4,'Yuri','Petrov','yuri@luv2code.com'),
(5,'Juan','Vega','juan@luv2code.com');Create Project
Dependency 를 위와 같이 포함시킨 뒤, project 를 generate 하자.
Development Process
Development Process 는 우선 다음 단계를 따라서 진행한다.
- Update DB configs in
application.properties- Create Employee entity (entity class)
- Create DAO interface
- Create DAO implementation
- Create REST controller to use DAO
처음에는 아래와 같은 Architecture 로 구성된다.
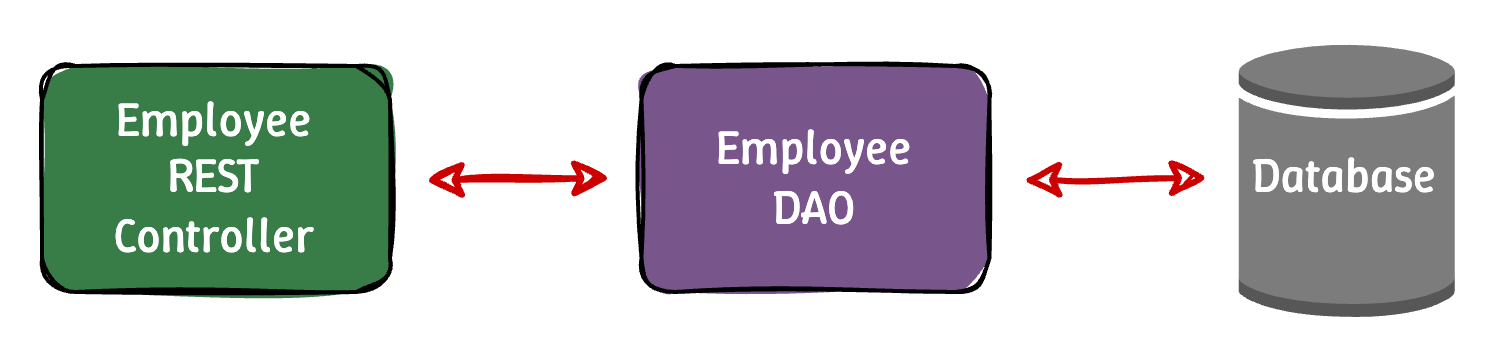
이전에 DAO 를 처음 다뤘을 때와 같이, DAO 를 Controller 에서 직접 injection 받아서 사용하는 구조이다. 이제 Development Process 에 있는 단계들을 하나씩 구현해보자.
우선 Database configuration 을 다음과 같이 application.properties 에 update 한다.
# JDBC properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/employee_directory
spring.datasource.username=username
spring.datasource.password=password그리고 Database Design 한 것을 기반으로 Entity Class 를 작성한다. Employee.java 에 다음과 같이 작성한다.
@Entity
@Table(name="employee")
public class Employee {
// define fields
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
private int id;
@Column(name="first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name="last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name="email")
private String email;
// define constructors
...
// define getter/setter
...
// define toString
...
}이렇게 @Entity 를 사용하여 JPA 가 알아서 실제 DB 의 employee table 및 각 field 와 mapping 을 수행하도록 하면 entity class 설정은 끝났다. 이제는 DAO 를 위한 Interface 와 그에 대한 Implementation 을 만들자.
이쯤에서 다시 Boss 가 요청한 API Requirements 를 확인해보자.
Create a RET API for the Employee Directory
REST clients should be able to
- get a list of employees
- get a single employee by id
- add a new employee
- update an employee
- delete an employee
requirements 의 첫 번째 사항부터 하나씩 구현하는 식으로 진행하면 좋을 것 같다. 다시 DAO 로 돌아와서, 모든 employee 의 list 를 return 할 수 있는 method 부터 declare 하고, define 하면 될 것 같다.
EmployeeDAO.java interface 에는 다음과 같이 작성하고,
public interface EmployeeDAO {
List<Employee> findAll();
}이를 implement 하는 EmployeeDAOImpl.java 에는 다음과 같이 작성하면 될 것이다.
@Repository
public class EmployeeDAOImpl implements EmployeeDAO {
// define field for entity manager
private EntityManager entityManager;
// set up constructor injection
public EmployeeDAOImpl(EntityManager entityManager) {
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
@Override
public List<Employee> findAll() {
// create a query
TypedQuery<Employee> theQuery = entityManager.createQuery("from Employee", Employee.class);
return theQuery.getResultList();
}
}마지막으로, 해당 DAO 를 Injection 받아 사용하는 REST Controller 를 작성하면 requirement 하나의 Development Process 가 끝이 난다. EmployeeRestController.java 에는 다음과 같이 작성한다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class EmployeeRestController {
private EmployeeDAO employeeDAO;
// quick and dirty: inject employee dao using constructor injection
public EmployeeRestController(EmployeeDAO employeeDAO) {
this.employeeDAO = employeeDAO;
}
// expose "/employees" and return a list of employees
@GetMapping("/employees")
public List<Employee> findAll() {
return employeeDAO.findAll();
}
}Potential Problem
그러나 잠재적인 문제점이 보이는 것 같다. 만약에 Buiness logic 이 조금 더 복잡해져서 하나의 method 에 여러개의 DAO 가 사용되고, logic 이 복잡해지면 Controller 내부의 code 가 무한히 늘어나 유지보수에 어려움이 생길 것이다.
그렇다면 Controller 와 Buisness logic 을 분리시킬 필요가 있을 것 같다.